Overview
The primary focus of this article is to delineate the essential ADA sink requirements that architects must adhere to in order to ensure compliance and enhance accessibility within restroom designs. It underscores the significance of specific measurements, including:
- Height specifications
- Clear floor space
- User-friendly faucet designs
Collectively, these elements facilitate ease of use for individuals with disabilities, thereby fostering an inclusive environment in public restrooms.
Introduction
Architects encounter the critical task of ensuring that restroom designs comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) sink requirements, a challenge that intricately weaves legal compliance with the creation of inclusive spaces. As accessibility emerges as a priority in modern architecture, a thorough understanding of the nuances of ADA regulations becomes essential for fostering environments that welcome all users.
What key elements must architects consider to not only meet these standards but also enhance the user experience in public restrooms? This article delves into the essential ADA sink requirements, offering insights that empower architects to design functional and aesthetically pleasing facilities while steering clear of common pitfalls.
The Splash Lab: Premium ADA-Compliant Sinks for Modern Restrooms
The Splash Lab USA excels in crafting premium sinks that adhere to ADA sink requirements, seamlessly integrating functionality with aesthetic appeal. Their innovative designs not only adhere to legal standards but also significantly enhance the user experience in contemporary bathroom settings.
With a robust commitment to sustainability and user-centric features, The Splash Lab has established itself as a reliable partner for architects and designers dedicated to creating inclusive sanitation environments. Recent surveys indicate that approximately 75% of architects prioritize ADA compliance in their restroom designs, recognizing its vital role in promoting accessibility and inclusivity.
Notably, initiatives such as Padel Haus in New York and Lacuna Space in California showcase The Splash Lab's ability to deliver tailored solutions that meet ADA sink requirements, emphasizing accessible layouts that enhance usability for all visitors.
As industry experts emphasize, the significance of ADA compliance, including the ADA sink requirements, cannot be overstated; it not only ensures legal adherence, helping businesses avert potential lawsuits, but also cultivates a welcoming atmosphere for all users.
The latest trends in ADA basin design reflect a dedication to user-friendliness, incorporating lever handles and motion-sensing technology that require minimal effort to operate.
By choosing The Splash Lab, architects and designers can confidently create washroom areas that are both compliant and inviting, ultimately enhancing the overall experience for everyone.
Height Specifications: ADA Sink Height Requirements for Accessibility
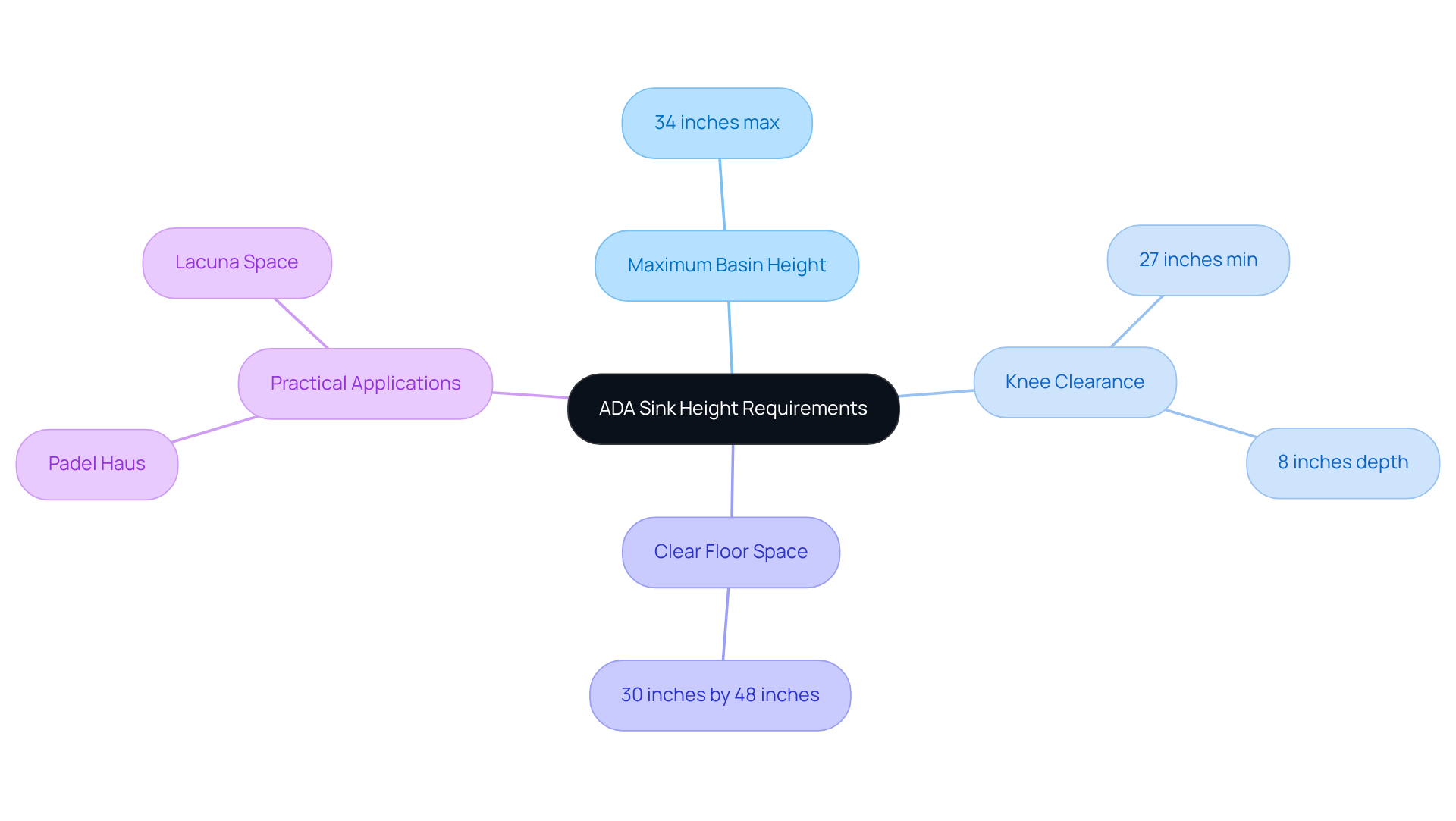
The maximum height for basin rims in public restrooms should not exceed 34 inches, as stated in the ADA sink requirements. This specification is vital for ensuring that individuals using wheelchairs can comfortably reach the basin. Furthermore, basins must be installed with sufficient knee clearance beneath them, requiring a minimum of 27 inches from the floor to the underside. This consideration facilitates ease of use and encourages inclusivity in washroom settings.
In addition to height requirements, it is essential to maintain a clear floor space of at least 30 inches by 48 inches in front of the sink to facilitate maneuverability for wheelchair users. This space is critical for ensuring that individuals can navigate comfortably and safely. The depth of knee space must also be at least 8 inches to accommodate mobility aids effectively. These dimensions are not merely recommendations; they are essential for compliance with ADA sink requirements, which aim to eliminate barriers and enhance accessibility for all patrons.
Practical applications of these guidelines can be observed in various bathroom layouts that emphasize ADA compliance. For example, initiatives such as Padel Haus in New York and Lacuna Space in California have effectively incorporated these height specifications, demonstrating how careful planning can produce functional and visually appealing bathroom environments that adhere to ADA regulations.
Accessibility advocates underscore the significance of following these height regulations, stating that ADA sink requirements for appropriate basin height are essential for fostering an inclusive environment in public restrooms. As Lester Nono articulates, "ADA compliance encompasses a wide range of guidelines, including architectural specifications, operational practices, and ongoing maintenance procedures." By prioritizing these specifications, architects can ensure that their designs not only meet legal requirements but also enhance the overall user experience for individuals with disabilities.
Clear Floor Space: Essential ADA Sink Accessibility Guidelines
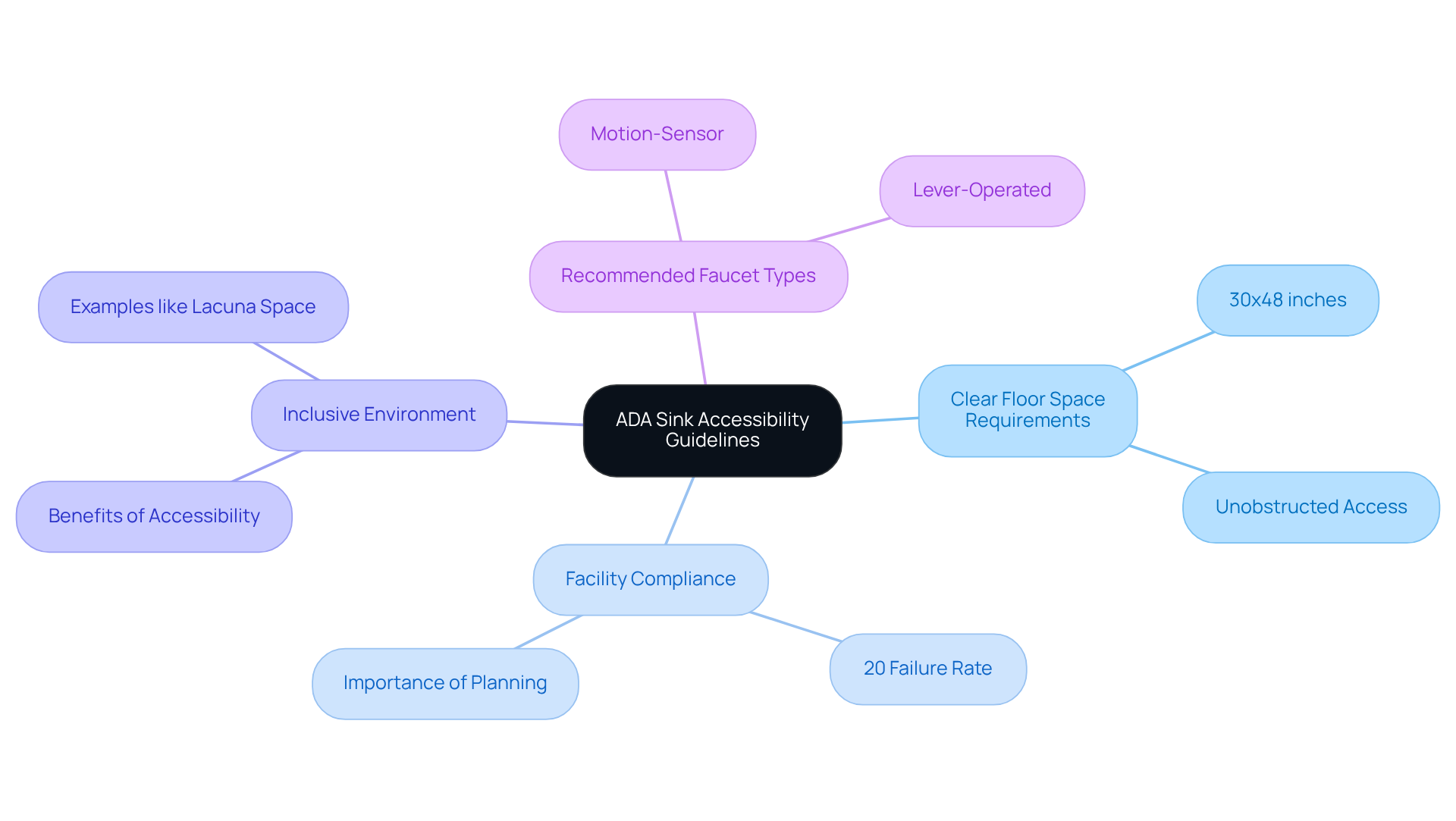
The ADA sink requirements mandate a minimum clear floor space of 30 inches by 48 inches in front of sinks to facilitate comfortable access for wheelchair users. This designated area must remain unobstructed, allowing individuals to navigate freely without encountering barriers. Facility managers emphasize that clear access is essential for ensuring that all users can effectively utilize washroom facilities. In fact, studies indicate that roughly 20% of facilities fail to meet these ADA sink requirements, underscoring the critical need for careful planning in layout.
The importance of clear floor space extends beyond mere compliance; it is vital for fostering an inclusive environment. Accessible restroom layouts, such as those implemented in projects like Lacuna Space, illustrate how thoughtful arrangement and unobstructed areas can significantly enhance usability for all individuals. Furthermore, incorporating recommended faucet types for ADA-compliant sinks—such as lever-operated and motion-sensor options—can greatly improve accessibility and usability. By prioritizing open floor space and considering these additional factors, architects can ensure that their designs not only meet the ADA sink requirements but also cultivate a welcoming environment for everyone.
Faucet Design: ADA Requirements for User-Friendly Operation
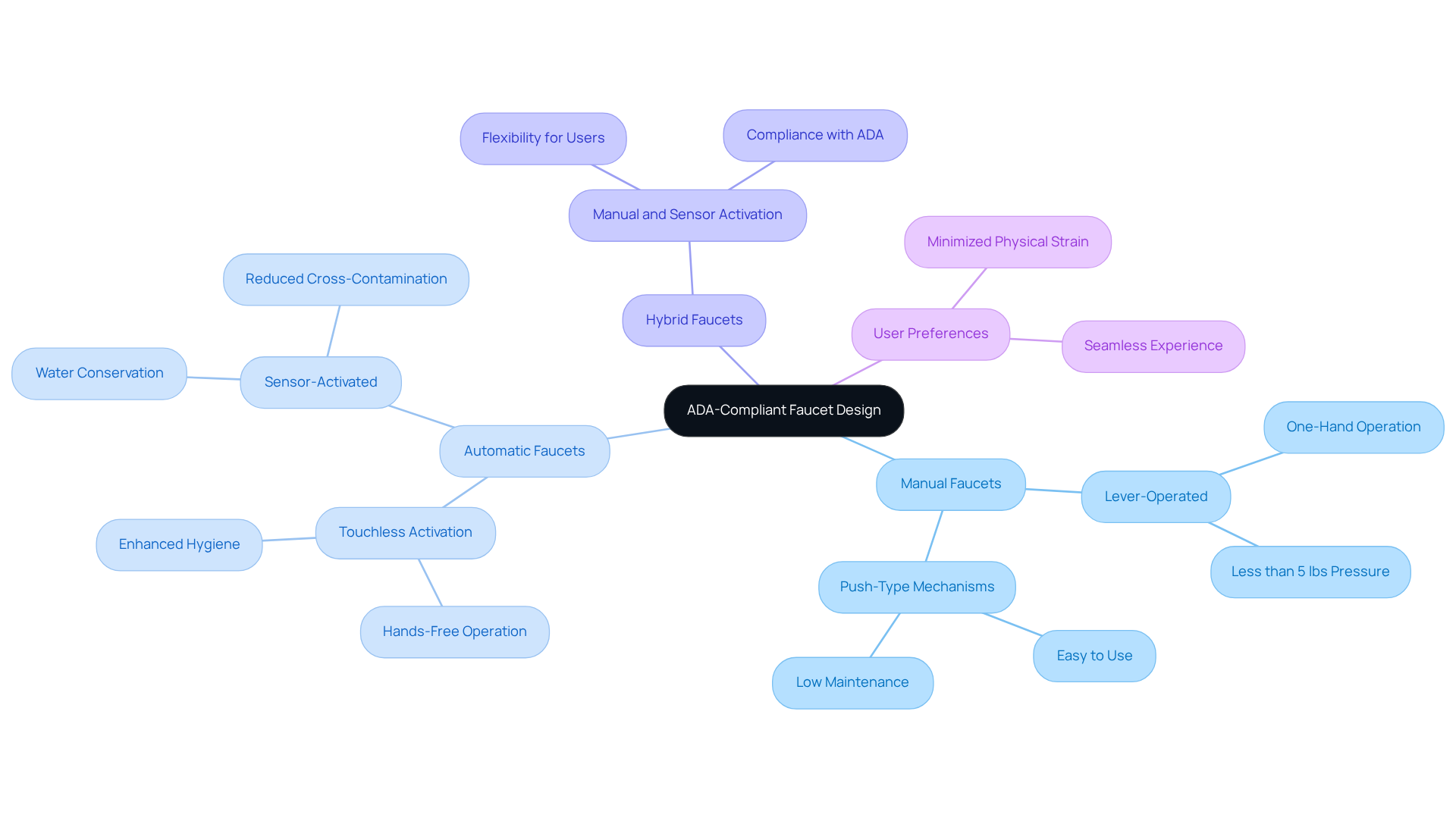
Faucets that adhere to ADA sink requirements must be operable with one hand, requiring no firm grasping, pinching, or wrist twisting. Furthermore, they should function with less than 5 lbs of pressure to accommodate individuals with limited strength. Lever-operated faucets stand out as particularly effective, allowing users with diminished hand strength to manipulate them easily, making them a preferred option across various settings. Recent innovations have led to the introduction of automatic faucets that activate via sensors, significantly enhancing accessibility by removing the need for manual operation. These touchless designs not only cater to individuals with disabilities but also promote cleanliness and convenience for all users, as they improve water conservation and reduce the likelihood of cross-contamination.
User preferences are increasingly shifting towards automatic faucets that fulfill ADA sink requirements in ADA-compliant environments, as they deliver a seamless experience while minimizing physical strain. Designers advocate for these solutions, highlighting their compliance with modern accessibility standards and their contribution to an improved overall bathroom experience. For instance, hybrid faucets that integrate both manual and sensor activation provide flexibility, accommodating a diverse range of user needs while ensuring compliance with ADA sink requirements.
Examples of user-friendly faucet designs in ADA-compliant facilities include those equipped with lever handles and touchless activation, which are favored for their ease of use and low maintenance requirements. Additionally, ensuring clear space around the faucet for wheelchair users is essential, facilitating easy access. By prioritizing these features, architects can create inclusive environments that not only meet regulatory standards but also enhance the functionality and aesthetics of commercial restrooms.
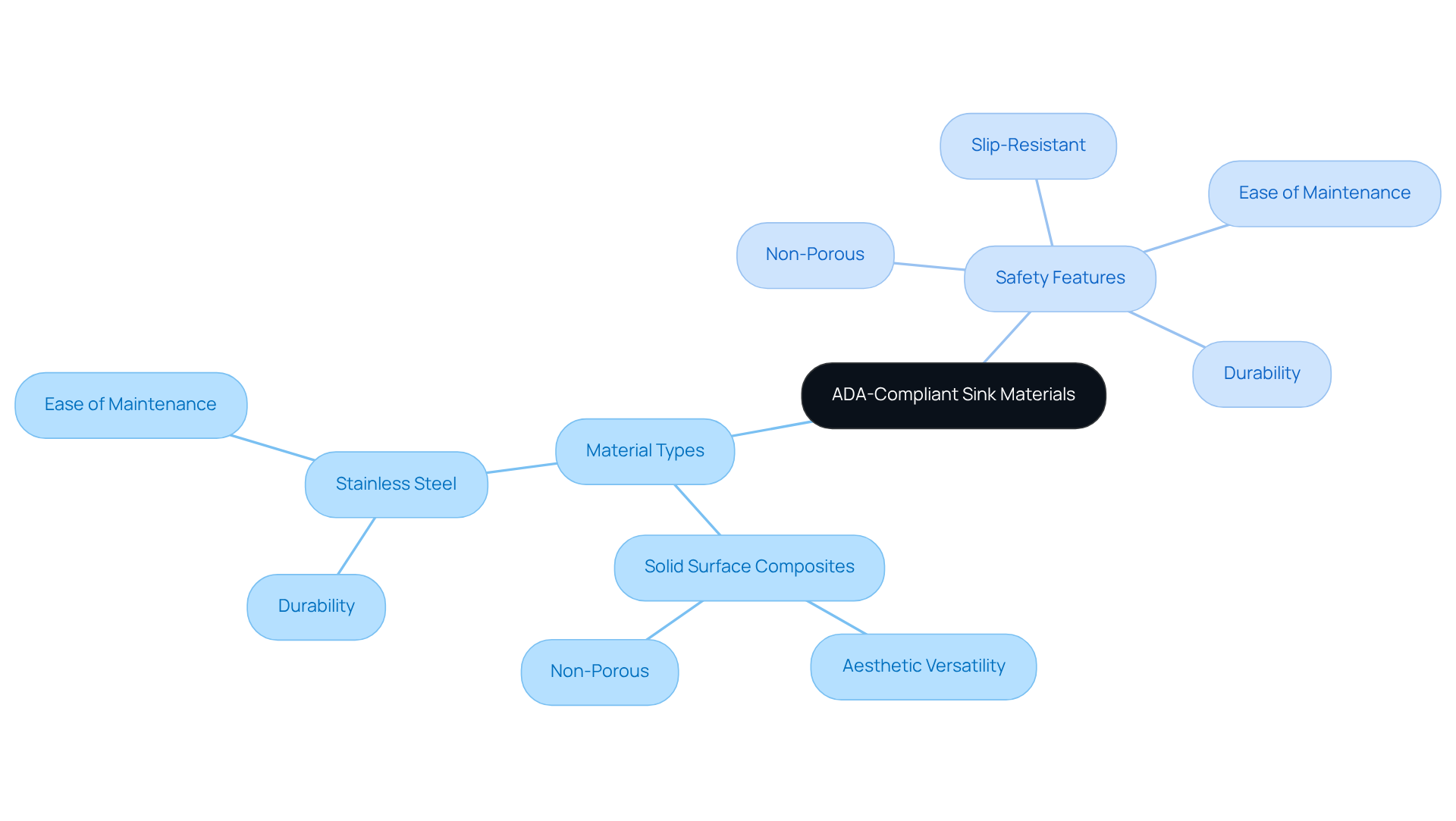
Material Selection: ADA-Compliant Sink Materials for Longevity and Safety
ADA-compliant basins must be constructed from robust, non-porous materials that facilitate easy cleaning and maintenance. Recommended materials include solid surface composites and stainless steel, both celebrated for their durability and resistance to bacteria. Health and safety expert Peter Ranney asserts, 'An ADA-compliant bathroom basin must adhere to the ADA sink requirements, which state it should be no higher than 34 inches, with at least 27 inches of knee clearance and 30 inches of clear floor space for wheelchair access.' These materials not only ensure a hygienic environment but also enhance the overall safety of washroom designs by being devoid of sharp edges, a crucial consideration for users with limited mobility.
Furthermore, recent data indicates that while solid surface composites provide aesthetic versatility, stainless steel remains the preferred choice for its unparalleled durability and ease of maintenance, making it particularly suitable for high-traffic environments. In addition, incorporating slip-resistant surfaces is vital for enhancing safety in ADA-compliant bathrooms. By selecting the appropriate materials, architects can design basins that satisfy ADA sink requirements, which enhances both functionality and safety in commercial facilities, aligning with The Splash Lab's commitment to quality craftsmanship and sustainability.
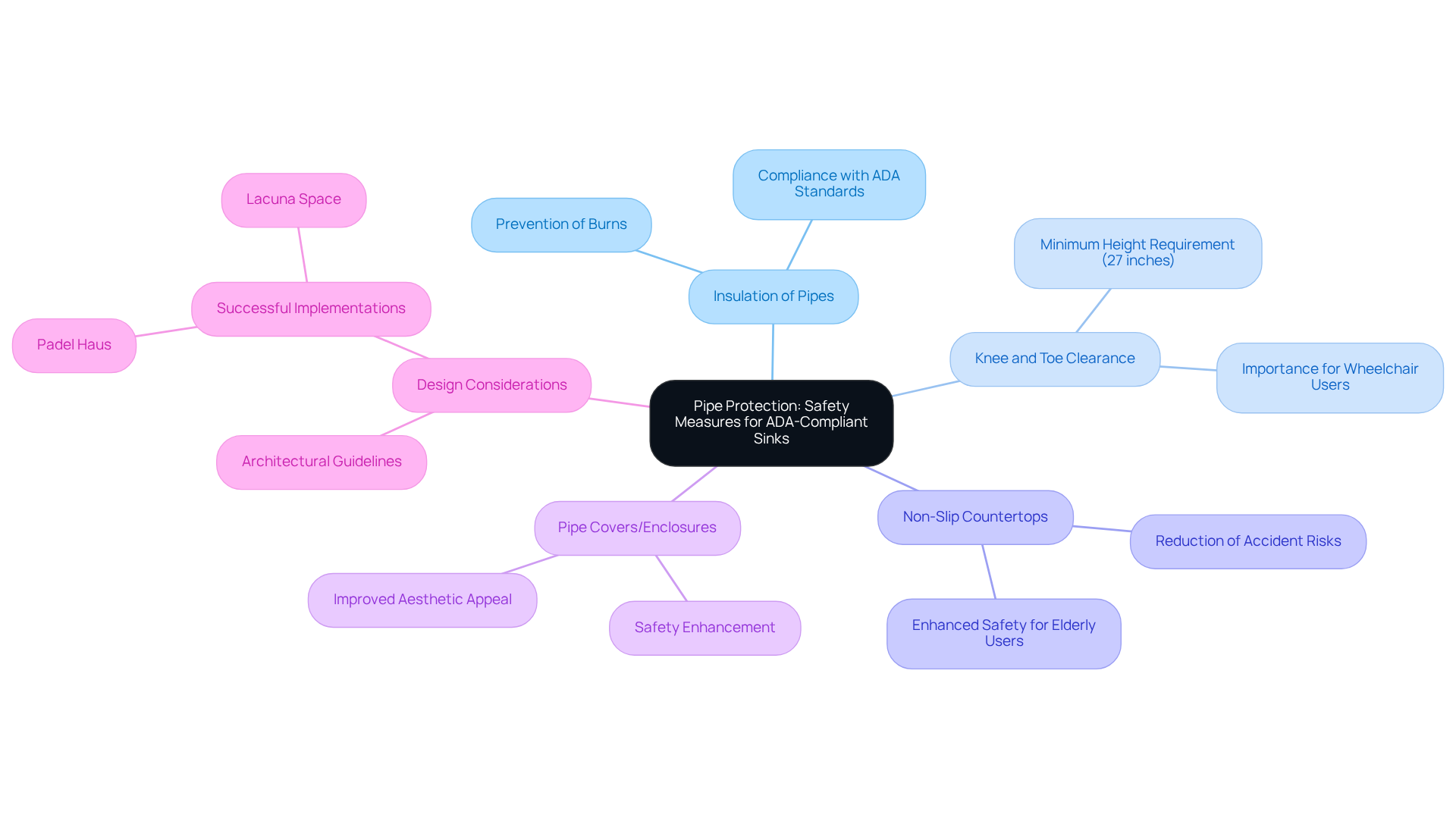
Pipe Protection: Safety Measures for ADA-Compliant Sinks
To comply with ADA sink requirements, it is crucial that exposed pipes under sinks are insulated or otherwise shielded to prevent contact. This includes ensuring that knee and toe clearance is devoid of sharp edges or hot surfaces, which can pose significant risks. Protective coverings not only reduce these hazards but also improve bathroom safety.
For instance, non-slip countertops diminish the risk of accidents while aligning with ADA compliance by providing a safer surface, particularly in facilities catering to elderly users. Furthermore, the installation of pipe covers or enclosures is recommended to enhance safety while maintaining a clean aesthetic.
By applying these safety measures, including adhering to the ADA sink requirements for knee clearance of at least 27 inches high, architects can develop restroom layouts that are compliant with ADA standards and prioritize user safety and comfort. Successful executions of these measures can be observed in projects such as Padel Haus and Lacuna Space, demonstrating how careful planning can improve accessibility.
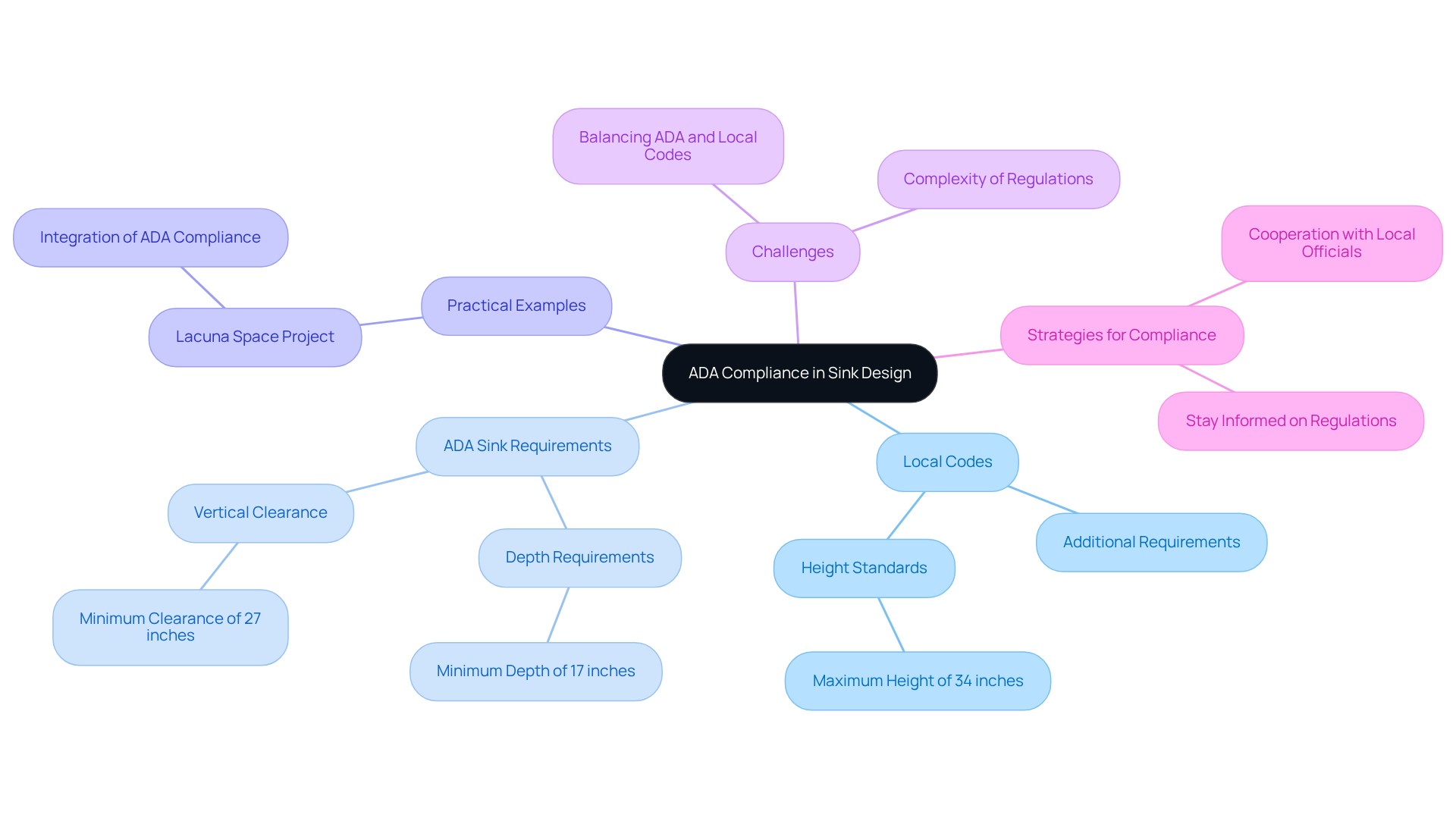
Local Codes: Navigating ADA Compliance in Sink Design
While the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) establishes essential accessibility standards, local building codes often introduce additional requirements, such as ADA sink requirements, that architects must navigate. Familiarity with these regulations is crucial to ensure that designs not only comply with ADA standards but also fulfill the ADA sink requirements. For instance, local regulations may specify certain height standards for basins, which generally should not surpass 34 inches from the ground, and require a minimum of 27 inches of vertical space beneath the basin to accommodate wheelchair users. Furthermore, the ADA sink requirements state that basins in accessible facilities must be at least 17 inches deep, a vital criterion for ADA compliance.
In practice, projects like the Lacuna Space in California exemplify how architects can successfully integrate ADA compliance with local codes. This project necessitated thorough evaluation of both ADA guidelines and local regulations, ensuring that all washroom fixtures, including basins, met the ADA sink requirements for accessibility and usability.
Architects often face challenges in balancing ADA compliance with local codes. As noted by industry professionals, the complexity of these regulations can lead to confusion. For example, while the ADA states that basins in accessible restrooms must be at least 17 inches deep, local regulations may impose extra requirements that necessitate further modifications. One architect remarked, "Navigating the intersection of ADA standards and local codes can be daunting, but it’s essential for creating truly accessible spaces."
To effectively navigate these local codes, architects should stay informed about any changes in building regulations related to ADA sink requirements. Frequent evaluations of local regulations and cooperation with local officials can offer clarity and guarantee that all plans are compliant. By prioritizing both ADA standards and local requirements, architects can create inclusive bathroom environments that enhance accessibility for all users.
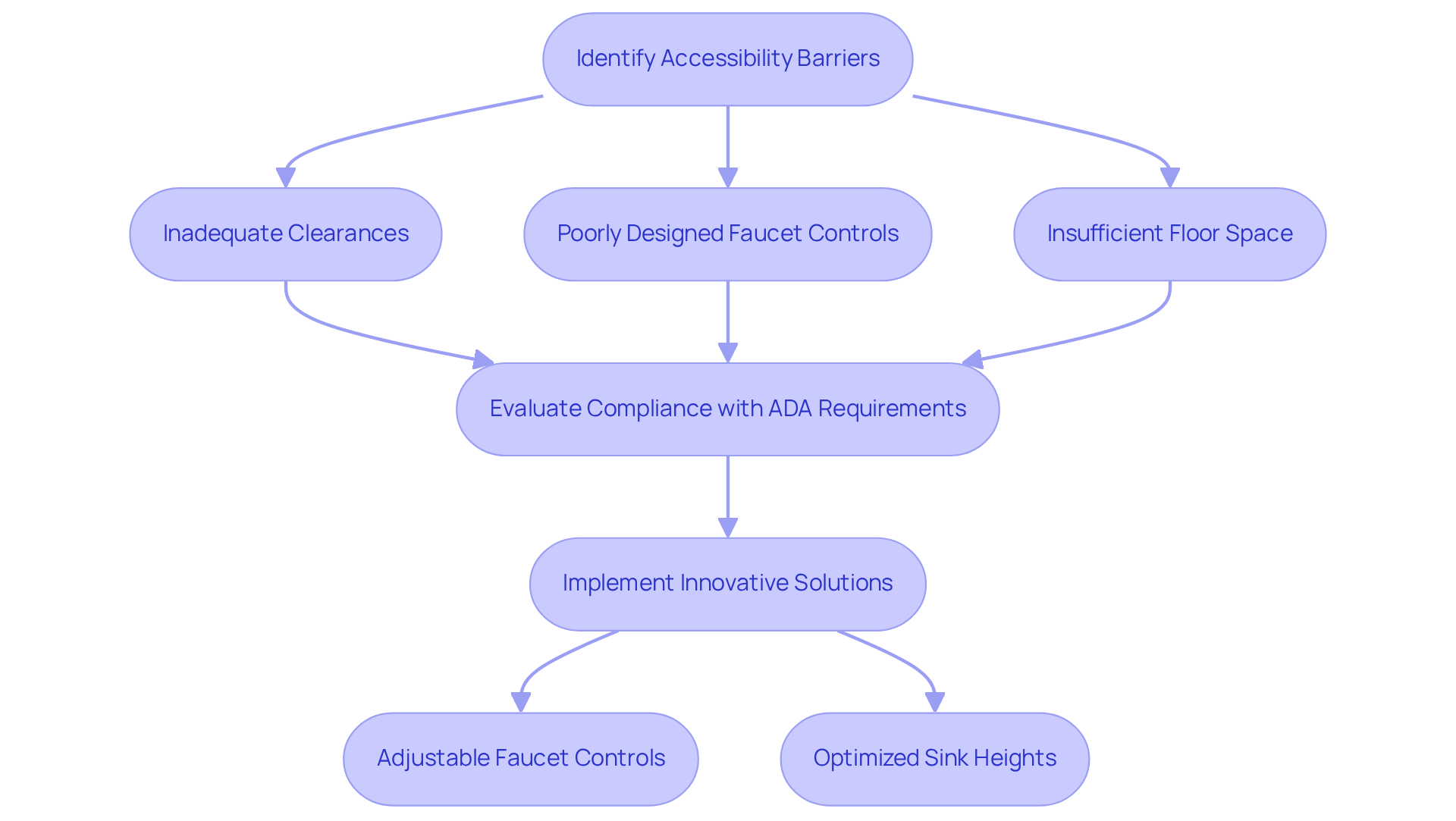
Barrier Identification: Recognizing Accessibility Challenges in Sink Design
Architects play a crucial role in identifying potential barriers that may hinder accessibility in restroom planning. Common challenges include inadequate clearances, poorly designed faucet controls, and insufficient floor space, significantly impacting usability for individuals with disabilities. For instance, to comply with ADA sink requirements, sinks must be positioned no higher than 34 inches, with knee clearance of at least 27 inches high, 30 inches wide, and 19 inches deep to accommodate wheelchair users effectively. Furthermore, faucet controls should be operable with one hand, requiring minimal effort to ensure ease of use for all individuals.
Accessibility consultants highlight the significance of performing comprehensive evaluations during the planning stage to identify these problems. As industry specialists emphasize, numerous ADA compliance difficulties arise from obsolete layouts and a lack of understanding concerning current standards. For example, a significant number of facilities fail to provide the necessary clear floor space of at least 60 inches, which is essential for wheelchair maneuverability. By proactively tackling these structural issues, architects can create inclusive spaces that not only fulfill legal standards but also enhance the overall experience for all users.
Successful projects, such as those completed by The Splash Lab, demonstrate how innovative solutions can overcome obstacles in ADA-compliant facility design. As Brent Otsuka, Manager of Interior Design at Fentress Architects, states, "The Splash Lab has well crafted and beautifully designed products. I always go to them first to create a comprehensively designed bathroom." The Splash Lab's products, including adjustable faucet controls and optimized sink heights, are designed to specifically address common challenges like inadequate clearances while complying with ADA sink requirements. By adhering to the ADA sink requirements, architects can ensure that facilities are accessible, functional, and visually appealing, ultimately promoting dignity and independence for all users. Consider exploring The Splash Lab's offerings to enhance your restroom layouts and ensure compliance.
Common Mistakes: Avoiding Pitfalls in ADA Sink Compliance
Frequent errors in adhering to ADA sink requirements often stem from overlooking critical criteria such as knee clearance, inadequate clear floor area, and the selection of faucet styles that are challenging to operate. The ADA sink requirements mandate that basins must provide a minimum of 27 inches of clear space from the floor to the underside, ensuring accessibility for wheelchair users. Additionally, a minimum ground space of 48 inches by 30 inches is required to comfortably meet the ADA sink requirements for approaching any sink element.
Architects must prioritize regular evaluations of their plans against ADA standards to proactively identify and address these issues. This practice not only mitigates the risk of costly lawsuits—particularly in states like California, which experiences a high volume of accessibility-related legal actions—but also enhances the usability of restroom facilities for the approximately 26% of Americans living with disabilities. Non-compliance with ADA sink requirements exposes businesses to significant legal risks, making it imperative to adhere to these standards.
Incorporating lessons learned from past ADA compliance failures can greatly improve project outcomes. A case study involving the Padel Haus project underscores the importance of selecting user-friendly faucet designs, such as lever-operated or motion-sensor options, which require minimal effort to operate. Furthermore, the Lacuna Space project exemplifies The Splash Lab's commitment to developing accessible sanitation facilities. By avoiding common pitfalls and adhering to ADA guidelines—such as ensuring that faucet activation requires no more than 5 pounds of pressure—architects can design functional, stylish, and compliant bathroom environments that effectively serve all users. Engaging a CASp Inspector for thorough inspections is also advisable to ensure compliance and avert potential challenges.
Comprehensive Planning: Strategies for Designing ADA-Compliant Sinks
To achieve ADA compliance, architects must embrace a comprehensive planning strategy that prioritizes early collaboration with stakeholders, thorough site assessments, and ongoing compliance evaluations throughout the development process. Engaging with project managers and consultants specializing in ADA compliance fosters a multi-stakeholder approach, ensuring that diverse needs are addressed effectively. Brent Otsuka, Manager of Interior Aesthetics at Fentress Architects, emphasizes that the successful creation of restrooms hinges on understanding the needs of all users, stating, "The Splash Lab has well-crafted and beautifully created products." He consistently turns to them first to design a comprehensively planned bathroom, highlighting the significance of cooperative methods in achieving practical and inclusive designs. Cameron Sinclair similarly underscores the importance of extracting needs from various stakeholders to create solutions that are both functional and inclusive.
Utilizing advanced tools such as CAD and BIM is crucial in this process. These technologies empower architects to develop detailed 3D models that visualize the ADA sink requirements, ensuring that all aspects of sink design—such as height, clearance, and accessibility features—are both functional and compliant. Data indicates that over 73% of establishments fail to meet ADA standards, and nearly 60.4% of individuals with disabilities in the USA encounter serious difficulties or are unable to access certain public buildings due to a lack of accessibility features. This underscores the pressing need for meticulous planning and execution.
Case studies from The Splash Lab illustrate the successful application of these principles. Their initiatives, including customized bathroom solutions for Padel Haus and Lacuna Space, demonstrate how thorough planning and collaboration with stakeholders lead to innovative creations that adhere to ADA standards while enhancing user experience. Furthermore, incorporating CASp inspections into the planning process is essential for proactively identifying and addressing compliance issues. By integrating these strategies, architects can ensure that their restroom designs not only comply with regulations but also promote inclusivity and accessibility for all users, fulfilling their moral obligation to provide accessible environments.
Conclusion
Architects play a pivotal role in creating restroom designs that not only comply with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) sink requirements but also promote inclusivity and accessibility. By understanding essential specifications—such as height limitations, clear floor space, and user-friendly faucet designs—architects can develop facilities that cater to all individuals, including those with disabilities. The integration of thoughtful design elements alongside compliance with ADA regulations is crucial for fostering welcoming environments in public restrooms.
Key insights from this article underscore the importance of adhering to ADA sink requirements, which encompass various aspects such as height specifications, clear floor space, and appropriate material selection. The emphasis on user-friendly faucet designs, safety measures for plumbing, and the navigation of local codes further illustrates the complexities involved in creating accessible restroom facilities. Successful projects, like those from The Splash Lab, serve as exemplary models of how architects can implement these guidelines effectively while enhancing overall user experience.
Ultimately, the commitment to ADA compliance is not merely a legal obligation; it is a moral imperative that reflects a dedication to inclusivity. Architects are encouraged to prioritize comprehensive planning and collaboration with stakeholders to ensure that restroom designs meet both ADA standards and the needs of all users. By embracing these principles, architects can significantly contribute to a more accessible world, promoting dignity and independence for everyone who utilizes public restroom facilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is The Splash Lab known for?
The Splash Lab is known for crafting premium ADA-compliant sinks that integrate functionality with aesthetic appeal, enhancing user experience in modern restroom settings.
Why is ADA compliance important in restroom design?
ADA compliance is important as it ensures legal adherence, helps businesses avoid potential lawsuits, and promotes accessibility and inclusivity for all users.
What are the height specifications for ADA-compliant sinks?
The maximum height for basin rims in public restrooms should not exceed 34 inches, and there must be a minimum of 27 inches of knee clearance from the floor to the underside of the basin.
What is the required clear floor space in front of ADA sinks?
A minimum clear floor space of 30 inches by 48 inches is required in front of sinks to facilitate comfortable access for wheelchair users.
How do recent trends in ADA basin design enhance usability?
Recent trends incorporate user-friendly features such as lever handles and motion-sensing technology that require minimal effort to operate, improving accessibility.
What are some examples of projects that showcase ADA compliance?
Examples include Padel Haus in New York and Lacuna Space in California, which effectively incorporate ADA sink requirements and emphasize accessible layouts.
What percentage of facilities fail to meet ADA sink requirements?
Studies indicate that roughly 20% of facilities fail to meet ADA sink requirements, highlighting the need for careful planning in restroom layouts.
How can architects enhance the experience for individuals with disabilities?
By prioritizing ADA specifications in their designs, such as appropriate basin height and clear floor space, architects can create inclusive and welcoming restroom environments.




